Friday, July 29, 2016
Saturday, July 23, 2016
The basics of keyboard shortcuts on Mac
Keyboard shortcuts Mac owners need to know: The basics
As Apple explains, keyboard shortcuts that are OS-wide or app-specific enable you to do things that you’d normally need a mouse, trackpad, or other input device to accomplish. On a Mac, keyboard shortcuts are activated by holding down one or more modifier keys and then pressing the last key of the shortcut. The modifier keys that you need to know as a Mac owner are:
- Command ⌘
- Shift ⇧
- Option ⌥
- Control ⌃
- Caps Lock ⇪
- Fn
If you’re using a keyboard that’s made for Windows PCs, you’ll simply hit the Alt key instead of Option, and the Windows logo key instead of Command. Some Mac keyboard and shortcuts also involve the special keys on the top row of the keyboard, including icons for volume, display brightness, and other functions. You’ll just press the icon key to perform that function, or combine it with the Fn key to use it as an F1, F2, F3, or other standard function key.
The Mac keyboard shortcuts ahead are the commands that any Mac owner should know. For most users, the most important categories of keyboard shortcuts are the basic commands that streamline things across the operating system, as well as the commands that make creating and editing documents easier. This is by no means an exhaustive list, but ahead are the essential keyboard shortcuts you should know on a Mac.
- Command-X, Command-C, and Command-V: These keyboard shortcuts will cut, copy, or paste, respectively. Cut will remove the selected item and copy it to the Clipboard, Copy will duplicate the selected item to the Clipboard, and Paste will paste the contents of the Clipboard into the current document or app.
- Command-Z and Command-Shift-Z: These keyboard shortcuts will undo the previous command, or reverse the undo command. Depending on the app, you may be able to undo and redo multiple commands.
- Command-A: Select All items.
- Command-F and Command-G: The Find command will open a Find window or find items in a document, while the Find Again command will find the next occurrence of an item that was previously found.
- Command-H and Command-M: The Hide command will hide the windows of the front app. (If you want to view the front app but hide the other open apps, press Command-Option-H.) The Minimize command will minimize the front window to the dock.
- Command-N: The New command will open a new document or window.
- Command-O: The Open command will open the selected item, or open a dialog to select a file to open.
- Command-P: Use this keyboard shortcut to print the current document.
- Command-S: This command will save the current document.
- Command-W: The Close command will close the front window, or you can press Command-Option-W to close all windows of the app.
- Command-Q and Option-Command-Esc: Command-Q will quit the app, while Option-Command-Esc will force-quit an app (one of the most useful keyboard shortcuts in the event of an unresponsive app).
- Command-Space bar: This is the keyboard shortcut to call up Spotlight search. It can show or hide the Spotlight search field.
- Space bar: Tapping the Space bar will use Quick Look to preview a selected item.
- Command-Tab or Shift-Command-Tilde (~): Command-Tab will switch apps, while Shift-Command-Tilde will switch to the next most-recent window of the front app.
- Shift-Command-3 or Shift-Command-4: These Screenshot commands will take a screenshot either of the entire screen or of the area that you select.
Keyboard shortcuts Mac owners need to know: Document shortcuts
- Command-B, Command-I, and Command-U: These keyboard shortcuts will bold, italicize, or underline the selected text.
- Command-T: This command will show or hide the Fonts window.
- Command-D: This shortcut will select the Desktop folder from within an Open dialog or Save dialog.
- Control-Command-D, Shift-Command-Colon (:), and Command-Semicolon (;): These keyboard shortcuts will show or hide the definition of a selected word, display the Spelling and Grammar window, or find misspelled words in a document.
- Option-Delete, Control-H, Control-D, and Control-K: These keyboard shortcuts will delete the word to the left of the insertion point, delete the character to the left of the insertion point, delete the character to the right of the insertion point, or delete the text between the insertion point and the end of the line or paragraph.
- Fn-Up Arrow, Fn-Down Arrow, Fn-Left Arrow, and Fn-Right Arrow: These keyboard shortcuts will scroll up one page, scroll down one page, scroll to the beginning of a document, or scroll to the end of the document.
- Command-Up Arrow, Command-Down Arrow, Command-Left Arrow, and Command-Right Arrow: These keyboard shortcuts will move the insertion point to the beginning of the document, to the end of the document, to the beginning of the current line, or to the end of the current line.
- Option-Left Arrow and Option-Right Arrow: These commands will move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word or to the end of the next word.
- Option–Shift–Up Arrow, Option–Shift–Down Arrow, Option–Shift–Left Arrow, and Option–Shift–Right Arrow: These keyboard shortcuts will extend the text selection to the beginning of the current paragraph, to the end of the current paragraph, to the beginning of the current word, or to the end of the current word.
- Control-A and Control-E: These command will move to the beginning of the line or paragraph or move to the end of a line or paragraph.
- Control-F and Control-B: These shortcuts will move one character forward or one character backward.
- Control-P and Control-N: These keyboard shortcuts will move up one line or down one line.
- Control-O: This command will insert a new line after the insertion point.
- Command–Left Curly Bracket ({), Command–Right Curly Bracket (}), and Shift–Command–Vertical bar (|): These keyboards will left-align, right-align, or center-align.
- Option-Command-C, Option-Command-V, and Option-Shift-Command-V: These keyboard shortcuts will copy the formatting settings of the selected item to the Clipboard, apply the copied style to the selected item, or apply the style of the surrounding content to the item pasted within that content.
win key 2
k
- Alt+Left arrow, Alt+Right arrow, Alt+Page Up, and Alt+Page Down: These keyboard shortcuts will go back, go forward, move up one screen, or move down one screen.
- Alt+Tab: This command enables you to switch between open apps.
- Ctrl+A: This command selects all of the items in a document or window.
- Ctrl+C (or Ctrl+Insert), Ctrl+D (or Delete), Ctrl+V (or Shift+Insert), and Ctrl+X: These keyboard shortcuts will copy the selected item, delete the selected item, paste the selected item, or cut the selected item.
- Ctrl+Z and Ctrl+Y: These keyboard shortcuts will undo and redo an action.
- Ctrl+Right arrow, Ctrl+Left arrow, Ctrl+Down arrow, and Ctrl+Up arrow: These keyboard shortcuts will move the cursor to the beginning of the next word, the beginning of the previous word, the beginning of the next paragraph, or the beginning of the previous paragraph.
- Ctrl+Shift with an arrow key: This command will select a block of text.
- Ctrl+Esc and Ctrl+Shift+Esc: These keyboard shortcuts open the Start Screen or the Task Manager.
- Shift+Delete: This command deletes the selected item without moving it to the Recycle Bin first.
- Right arrow or Left arrow: The Right arrow will open the next menu item to the right or open a submenu, while the Left arrow will open the next menu item to the left or close a submenu.
- Ctrl+Tab, Ctrl+Shift+Tab, and Ctrl+number: These keyboard shortcuts will move you forward through tabs, move back through tabs, or move to the nth tab.
- Tab and Shift+Tab: These commands enable you to move forward through options or move back through options.
- Alt+underlined letter: This shortcut performs the command or selects the option that goes with that letter.
- Spacebar: This key selects or clears the check box if the active option is a check box.
- Backspace: This key opens a folder one level up if a folder is selected in the Save As or Open dialog box.
window Key
- Ctrl+C (or Ctrl+Insert), Ctrl+X, and Ctrl+V (or Shift+Insert): Among the most basic keyboard shortcuts for Windows users, these standbys will copy, cut, or paste the selected item.
- Alt+Tab: This command will switch between open apps.
- Alt+F4: This shortcut will close the active item or exit the active app.
- Windows logo key
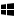 +L: This command will lock your PC or switch accounts.
+L: This command will lock your PC or switch accounts. - Windows logo key
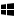 +D: This shortcut will display or hide the desktop.
+D: This shortcut will display or hide the desktop. - Windows logo key
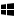 +start typing: This command enables you to search your PC. (Make sure you let off the Windows key before typing.)
+start typing: This command enables you to search your PC. (Make sure you let off the Windows key before typing.) - Ctrl+plus (+) or Ctrl+minus (-): These keyboard shortcuts enable you to zoom in and out of a large number of items, like apps pinned to the Start screen. (An alternative is pressing Ctrl and using the scroll wheel.)
- Windows logo key
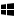 +C: This command opens the Charms, or if you’re in an app, it opens the commands for that app.
+C: This command opens the Charms, or if you’re in an app, it opens the commands for that app. - Windows logo key
 +Z: This keyboard shortcut shows the commands that are available within an app.
+Z: This keyboard shortcut shows the commands that are available within an app. - Windows logo key
 +Tab: This command enables you to cycle through recently used apps, while Windows logo key
+Tab: This command enables you to cycle through recently used apps, while Windows logo key  +Shift+Tab enables you to cycle through recently used apps in reverse order.
+Shift+Tab enables you to cycle through recently used apps in reverse order. - Esc: Tapping the escape key enables you to stop or exit the current task.
- F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6: These keys open Display Help, rename a selected item, search for a file or folder, display the address bar list in File Explorer, refresh the active window, or cycle through the screen elements in a window or on the desktop.
- F10: This key will activate the Menu bar in the active app.
- Alt+F4: This command will close the active item or exit the active app.
- Alt+Spacebar: This command will open the shortcut menu for the active window.
Tuesday, June 21, 2016
Win10各种注册表小设置
很多人不适应Win10的新功能,且还有强迫症,讨厌任务栏的搜索和多任务按钮。现提供屏蔽方法。
去除搜索按钮
复制粘贴一下内容,保存为reg文件,双击,确定(注意导入后需要重新启动资源管理器)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000000
如何你想恢复,导入如下即可(两个注册表任选其一即可恢复注意导入后需要重新启动资源管理器)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000000
或者导入
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000001
去除多任务(虚拟桌面)按钮(同一楼,复制粘贴保存为reg文件)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000
恢复多任务按钮
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000
或者
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
预览版更新选择功能,预览版微软锁定了选择权,现提供注册表方法更改
从不检查更新(不推荐)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000001
检查更新,但是让我选择是否下载和安装更新
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000002
下载更新,但是让我选择是否安装更新
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000003
自动安装更新(推荐)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000004
隐藏资源管理器主页内容
在主页中隐藏Frequent folder
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{3936E9E4-D92C-4EEE-A85A-BC16D5EA0819}]
在主页中显示Frequent folder(恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{3936E9E4-D92C-4EEE-A85A-BC16D5EA0819}]
@="Frequent Places Folder"
在主页中隐藏Recent files
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{4564b25e-30cd-4787-82ba-39e73a750b14}]
在主页中显示Recent files(就是恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{4564b25e-30cd-4787-82ba-39e73a750b14}]
@="Recent Items Instance Folder"
在主页中隐藏收藏夹
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{d34a6ca6-62c2-4c34-8a7c-14709c1ad938}]
在主页中显示收藏夹(就是恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{d34a6ca6-62c2-4c34-8a7c-14709c1ad938}]
@="Favorites Folder"
注册表开启Win10新任务栏时间日期面板
1.键盘快捷键WIN+R打开运行,输入regedit打开注册表编辑器
2.前往
游客,如果您要查看本帖隐藏内容请回复
3.创建新的DWORD(32-bit),名字为UseWin32TrayClockExperience,保持0值
4.点击任务栏右下角的时间和日期会打开新的面板,界面上的“其他时钟”可以打开闹钟应用里的“世界时钟”,但添加城市目前还不会在任务栏的时间日期面板里显示。
右键添加管理员权限
下面的代码保存成REG导入即可
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\runas]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\runas\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas2]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas2\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\runas]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\runas\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" /r /d y && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F /t"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" /r /d y && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F /t"
以上均为注册表项,都需要复制粘贴,保存为reg注册表格式文件,导入即可。
去除或恢复任务栏按钮的需要重启资源管理器。去除或恢复主页的不需要
去除搜索按钮
复制粘贴一下内容,保存为reg文件,双击,确定(注意导入后需要重新启动资源管理器)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000000
如何你想恢复,导入如下即可(两个注册表任选其一即可恢复注意导入后需要重新启动资源管理器)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000000
或者导入
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search]
"EnableProactive"=dword:00000001
去除多任务(虚拟桌面)按钮(同一楼,复制粘贴保存为reg文件)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000
恢复多任务按钮
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000
或者
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MultitaskingView\AllUpView]
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
预览版更新选择功能,预览版微软锁定了选择权,现提供注册表方法更改
从不检查更新(不推荐)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000001
检查更新,但是让我选择是否下载和安装更新
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000002
下载更新,但是让我选择是否安装更新
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000003
自动安装更新(推荐)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\Auto Update]
"AUOptions"=dword:00000004
隐藏资源管理器主页内容
在主页中隐藏Frequent folder
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{3936E9E4-D92C-4EEE-A85A-BC16D5EA0819}]
在主页中显示Frequent folder(恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{3936E9E4-D92C-4EEE-A85A-BC16D5EA0819}]
@="Frequent Places Folder"
在主页中隐藏Recent files
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{4564b25e-30cd-4787-82ba-39e73a750b14}]
在主页中显示Recent files(就是恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{4564b25e-30cd-4787-82ba-39e73a750b14}]
@="Recent Items Instance Folder"
在主页中隐藏收藏夹
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{d34a6ca6-62c2-4c34-8a7c-14709c1ad938}]
在主页中显示收藏夹(就是恢复原状)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\HomeFolder\NameSpace\DelegateFolders\{d34a6ca6-62c2-4c34-8a7c-14709c1ad938}]
@="Favorites Folder"
注册表开启Win10新任务栏时间日期面板
1.键盘快捷键WIN+R打开运行,输入regedit打开注册表编辑器
2.前往
游客,如果您要查看本帖隐藏内容请回复
3.创建新的DWORD(32-bit),名字为UseWin32TrayClockExperience,保持0值
4.点击任务栏右下角的时间和日期会打开新的面板,界面上的“其他时钟”可以打开闹钟应用里的“世界时钟”,但添加城市目前还不会在任务栏的时间日期面板里显示。
右键添加管理员权限
下面的代码保存成REG导入即可
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\runas]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\runas\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas2]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas2\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\runas]
@="管理员取得所有权"
"NoWorkingDirectory"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\runas\command]
@="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" /r /d y && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F /t"
"IsolatedCommand"="cmd.exe /c takeown /f \"%1\" /r /d y && icacls \"%1\" /grant administrators:F /t"
以上均为注册表项,都需要复制粘贴,保存为reg注册表格式文件,导入即可。
去除或恢复任务栏按钮的需要重启资源管理器。去除或恢复主页的不需要
USB标准
USB标准乱起名傻傻分不清 三句话理清乱象
十多年前,USB总线进入主流视野,提供了一个全新的存储方向,并用一个统一的标准把众多外设都全部拉入自己的阵营。这是他们为整个行业带来的巨大贡献,没有人会否认。但是推广USB的组织有着特殊的取名技巧,让人捉摸不透:十多年后的今天,进化了三个大版本的USB标准,不光搞出了一大堆别名,USB 3.1的出现还分出Gen1和Gen2,更别提那些mini、micro、Type-ABC的接口形态定义了。
这让我们这群普通人看得那叫一个疼,以往还从接口和插头的颜色一眼就判断出哪个是速度更快的,现在看着这些新冒出来的东西傻傻分不清楚,不想为USB-IF取名品味背锅的人们,是时候好好算一笔总账了。
Full?High?Super?抱歉我英语不太好……
回望USB从二十年前的1.0起,截至今天广泛为人所接受的3.0,USB标准总共经历了四个版本的迭代:1.0、1.1、2.0和3.0,光看阿拉伯数字的话,小学数学及格的人都能知道哪个版本更为先进。但USB-IF有一个起艺名的嗜好,他们给传输速率也起了名字:1.5Mbit/s叫Low Speed、12Mbit/s叫Full Speed、480Mbit/s叫Hi-Speed、5Gbit/s就是SuperSpeed,语言的冲击力可比冷冰冰的数字大多了。
很遗憾的是传输速率一定会和USB标准的版本挂钩,所以USB-IF觉得给几个USB版本直接上套速率的名字给称呼起来好像也挺带感,比如Hi-Speed USB和SuperSpeed USB。结果问题来了,当一个东西存在多种叫法的时候,一旦搅混就让人摸不着头脑。大家看起来都很快呀,我怎样才能知道哪一个是USB 3.0?
而且USB还有一个很棒的特性叫做向下兼容,所以USB-IF也就干脆让新标准“吃掉”老标准,然后把旧的传输速率也划分到新标准下面,所以在极少情况下你能看到像Full Speed USB 2.0这样的奇葩。
这一团乱麻本该是一个无法收拾的局面,好在USB-IF在推广USB 3.0的关头想到了出奇制胜的一招——改接口的颜色。他们决定让USB 3.0/SuperSpeed USB标准的设备统一采用蓝色作为接口塑料板的配色,以和旧标准的接口区分开来。群众一时间弹冠相庆,哪怕是近视都能一眼认出哪个接口标准更新速度更快了。下游硬件厂商虽然看着接插件又多了5个pin而感到肉痛,但咬咬牙上了新接口,推广效果相比成本的增加还是值得的。
强行把USB 3.1分成两代 在下心服口服
但好景不长,2013年Intel把Thunderbolt接口的两股数据流拧成一股,达到20Gbit/s的传输速率,USB-IF看着你速度都已是我4倍,深感不能忍。当年7月,USB组织公开USB 3.1标准。按照通常的逻辑,USB 3.1就是USB 3.0的升级,但在今天讨论USB 3.1是不是比USB 3.0更快,或是存在什么其他的进步却是一个不成立的话题,因为USB 3.0已经不存在于USB-IF的定义里了。留下的现行标准里,除了代表2.0标准的Hi-Speed USB外,只有SuperSpeed USB和SuperSpeed USB 10Gbps。
难道统治了外设及移动存储连接界好几年的USB 3.0标准就这么被宣布突然死亡了?显然不是,只是USB-IF的命名习惯实在太差。你刚刚应该在上面看到过,USB-IF还管USB 3.0叫SuperSpeed USB的,那如此看来这个SuperSpeed 10Gbps便是USB 3.1了?天真。USB 3.1 Gen 1和USB 3.1 Gen 2两兄弟华丽登场时,你最想做的事情就会是把USB-IF里负责起名字的人的脑袋给按进显示器。
所谓USB 3.1 Gen 1就是原来的USB 3.0,真正的新标准是这个叫USB 3.1 Gen 2的东西。至于传输速率的那个英文名,尽管USB-IF很喜欢,我们还是选择无视比较好。
单纯从纸面数据上看,USB 3.1 Gen 2标准把理论传输速率给翻了一倍赶上了第一代Thunderbolt,还在编码位宽从十位提升至百位的同时,把信令开销从原来的20%压低到了3%,可谓是长足进步。但这次下游厂商这次面对接受新标准所带来的成本和兼容性挑战时不干了,于是他们宁肯配合USB组织的命名障眼法“升级”USB 3.1,也不愿花大力气应用新接口。
所以现在绝大多数宣称支持“USB 3.1”标准,但不肯说明究竟是Gen 1还是Gen 2的电子产品或是PC配件,实际上骨子里都还是USB 3.0的能力。
你们不说 差点以为USB Type-C = USB 3.1
因为要适应不同的设备种类,在USB Type-C出现前,光从接口形态上来区分,USB 2.0标准的接口就有USB Type-A,USB Type-B,miniUSB Type-B、microUSB Type-A以及microUSB Type-B五种(已经被淘汰的不计在内),而在USB 3.0时代还新出现了USB 3.0 Type-A、USB 3.0 Type-B和microUSB 3.0 Type-B。
我们在日常生活中最常接触到的便是USB Type-A、USB 3.0 Type-A和microUSB Type-B。因为有颜色和形状的双重区分,人们还是能较容易地辨明接口的用途和速度。
但在2014年,USB IF发布了USB Type-C的1.0版定义,这个接口不仅仅是定义了一个不会插反的新接口形态,它24个的触点数目远超出现行USB标准定义的4个或9个,所以即便USB Type-C可以通过转接的形式兼容旧标准,但它并不是一个以适应现行USB标准为目的的接口,这个接口是为未来而准备的。由于USB Type-C几乎是和USB 3.1前脚跟着后脚出现的,再加上以前压根没人关心自己每天插来插去的USB接口是什么Type,结果不少人瞬间迷失,把二者混为一谈。
不过实际情况是USB 3.1 Gen 2只是一个传输标准,USB Type-C于它而言则只是一个合适的物理载体。USB Type-C也可以承载USB 2.0和USB 3.1 Gen 1协议,现在越来越多使用USB Type-C作为接口的智能手机就是很好的例子。
但USB Type-C能干的事情远不止以10Gbit/s的高速传输小电影:支持USB PD 2.0的USB Type-C能以20V/5A(100W)的大功率给笔记本这样的大户供电;而支持DP附加模式的USB Type-C可以外接兼容该模式的显示器;Intel甚至在第三代Thunderbolt标准的定义上选择与USB Type-C共用接口。
三句话理清USB标准乱象
现在可以用简单的几句话为全文作出总结:
1、USB 3.0接口通常为蓝色,一定会有5个以上的触点,而USB 2.0接口的触点不会超过5个;
2、USB 3.1 Gen1就是USB 3.0换了个马甲;
3、不要见到USB Type-C就以为它会更快,速度请认准USB 3.1 Gen2。
虽然USB最终的前进方向必定是往着USB Type-C/USB 3.1 Gen2走的,但一个新标准新接口的普及总会花上至少好几年的时间,将来我们必定会面对新老标准共存的混乱场面,先打好预防针,接下来几年内接触带USB接口设备时便可心中有数,拒绝被坑了。
Wednesday, January 6, 2016
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

